Chronic Muscle Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
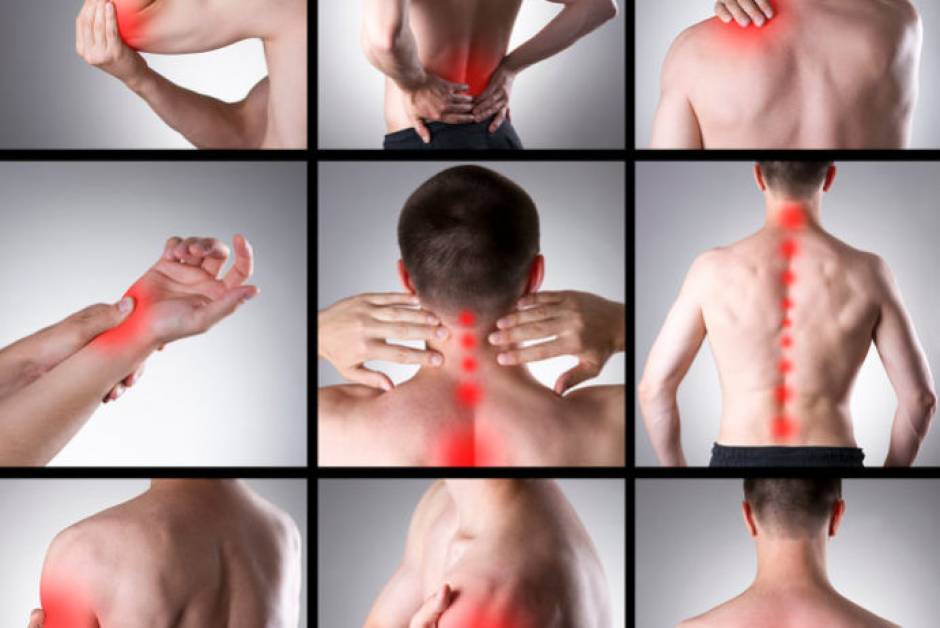
Introduction
Chronic muscle pain is a persistent condition that can significantly impact daily life and overall well-being. Unlike acute muscle pain, which resolves within a few days to weeks, chronic muscle pain lasts for months or even longer. This article delves into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for chronic muscle pain, providing a comprehensive guide for individuals seeking relief.
Understanding Chronic Muscle Pain
Chronic muscle pain, or myalgia, can affect specific muscles, groups of muscles, or the entire body. It is often associated with underlying medical conditions and can vary in intensity from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating pain.
Common Causes of Chronic Muscle Pain
- Fibromyalgia: A chronic condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness in localized areas.
- Myofascial Pain Syndrome: A condition where pressure on sensitive points in the muscles (trigger points) causes pain in seemingly unrelated body parts.
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: A disorder characterized by extreme fatigue that cannot be explained by any underlying medical condition.
- Arthritis: Inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, that affect the joints and surrounding muscles.
- Injuries and Overuse: Repeated muscle strain or trauma can lead to long-term pain.
- Infections: Some viral and bacterial infections can cause prolonged muscle pain.
- Neurological Disorders: Conditions like multiple sclerosis or peripheral neuropathy can contribute to chronic muscle pain.
Symptoms of Chronic Muscle Pain
The symptoms of chronic muscle pain can vary widely but often include:
- Persistent muscle aches and soreness
- Stiffness and limited range of motion
- Fatigue and difficulty sleeping
- Tenderness and sensitivity in affected areas
- Swelling and inflammation
- Muscle weakness
Diagnosis of Chronic Muscle Pain
Diagnosing chronic muscle pain involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Healthcare providers may use the following methods to identify the underlying cause:
- Blood Tests: To check for signs of inflammation, infection, or autoimmune conditions.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to visualize bone and soft tissue structures.
- Electromyography (EMG): To assess muscle and nerve function.
- Pain Mapping: Identifying specific areas of pain and trigger points.
Treatment Options for Chronic Muscle Pain
Effective management of chronic muscle pain often requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining medical treatments with lifestyle modifications and alternative therapies.
Medications
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage mild to moderate pain.
- Prescription Medications: For more severe pain, prescription medications like Pain O Soma 500mg or Pain O Soma 350mg may be used. These muscle relaxants work by affecting the central nervous system to reduce pain and muscle spasms.
- Antidepressants: Certain antidepressants, such as amitriptyline or duloxetine, can help alleviate chronic pain and improve sleep.
- Anti-seizure Medications: Drugs like gabapentin or pregabalin are effective in treating nerve-related pain.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of chronic muscle pain management. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to improve strength, flexibility, and endurance, helping to alleviate pain and prevent further injury.
Massage Therapy
Massage therapy can relieve muscle tension, improve circulation, and promote relaxation. Regular sessions with a professional therapist or self-massage techniques using foam rollers can be beneficial.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a form of psychotherapy that helps individuals manage pain by changing the way they think and respond to pain. It can be effective in reducing the emotional and psychological impact of chronic muscle pain.
Alternative Therapies
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to relieve pain and promote healing.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractic adjustments can help align the spine and improve overall musculoskeletal function, reducing muscle pain.
- Herbal Remedies: Certain herbs, like turmeric and ginger, have anti-inflammatory properties that can help manage chronic muscle pain.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Exercise: Regular low-impact exercise, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, can help maintain muscle strength and flexibility.
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients supports muscle health. Ensure adequate intake of protein, vitamins, and minerals.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help manage stress and reduce muscle tension.
Conclusion
Chronic muscle pain is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive and individualized approach to management. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring various treatment options, individuals can find effective ways to alleviate pain and improve their quality of life. For personalized advice and treatment plans, consult with a healthcare provider.

 Smile Brighter: Meet Canberra’s Top Dental Hygienists
Smile Brighter: Meet Canberra’s Top Dental Hygienists  Transform Your Comfort: Discover the Benefits of Cushions Lab Seat Cushions and Pillows
Transform Your Comfort: Discover the Benefits of Cushions Lab Seat Cushions and Pillows  Enhance Your Mental Clarity with Modafresh 200
Enhance Your Mental Clarity with Modafresh 200  List of Top 10 Neurologists in India 2024
List of Top 10 Neurologists in India 2024  Body Care Products Manufacturers: Providing Quality Products for Your Skincare Needs
Body Care Products Manufacturers: Providing Quality Products for Your Skincare Needs  The Journey to the Best Microblading in Dubai: A Client’s Perspective
The Journey to the Best Microblading in Dubai: A Client’s Perspective  Exploring London’s Best Butcher Shops
Exploring London’s Best Butcher Shops  Enhance Your Shop Appeal with Sydney’s Best Carpentry Services
Enhance Your Shop Appeal with Sydney’s Best Carpentry Services  A Detailed Look at the Features of the LEGO Technic Mars Crew Exploration Rover
A Detailed Look at the Features of the LEGO Technic Mars Crew Exploration Rover